Phosphate refers to the inorganic salt of phosphoric acid, a compound that contains the element phosphorus.
Phosphates are essential for various biological processes and are found in living organisms, as well as in rocks, soils, and water.
Large deposits of
phosphate rock exist in various parts of the world.
The processing of rock phosphate yields phosphoric acid, which is a precursor to various phosphate compounds.

Phosphate Uses
Phosphates have various important uses in different industries and applications.
Here are some common uses of phosphates:

Agriculture and Fertilizers:
Phosphates are a key component of fertilizers, providing essential nutrients (phosphorus) for plant growth.
They help promote root development, flowering, and fruiting.
Food Industry:
Phosphates are used as food additives for various purposes, such as:
- Buffering: Phosphates help control the acidity of food products.
- Emulsification: They assist in stabilizing emulsions in processed foods.
- Moisture Retention: Phosphates can improve the moisture retention of certain food products.
Water Treatment:
Phosphates are employed in water treatment to inhibit the formation of scale deposits and prevent corrosion in pipes and equipment.
They are also used to control algae growth in water bodies.
Detergents and Cleaning Products:
In household and industrial cleaning products, phosphates are used to enhance the effectiveness of detergents by softening water and improving the removal of dirt and stains.
Industrial Processes:
Phosphates play a role in various industrial processes, including metal treatment, electroplating, and the production of ceramics and glass.
Health and Nutrition:
Phosphates are an essential component of the human diet, contributing to bone and teeth health.
They are also involved in various metabolic processes, and phosphorus compounds like ATP (adenosine triphosphate) are critical for energy transfer in cells.
Flame Retardants:
Certain phosphate compounds are used as flame retardants in materials like plastics and textiles to reduce the risk of fire.
Construction Materials:
Phosphates are used in the production of construction materials, such as cement and drywall, to improve their properties.
Animal Feed:
Phosphates are added to animal feed to ensure proper nutrition for livestock.
They contribute to bone development and overall growth.
Medical Applications:
Phosphates are used in some medical applications, including in the formulation of certain medications and as a component in intravenous (IV) solutions.
How to Process Phosphate Powder?
The processing of phosphate powder can involve various steps depending on the intended use and the specific form of phosphate being processed. Phosphate powder may be derived from phosphate rock and is often processed for use in fertilizers, detergents, food additives, or other industrial applications. Here's a general overview of the process:

1. Mining and Extraction:
Phosphate Rock: The primary source of phosphate is phosphate rock, which is mined from deposits. The rock may undergo physical and chemical beneficiation processes to increase its phosphorus content.
2. Beneficiation:
Physical Methods: Techniques such as crushing, screening, and gravity separation may be used to concentrate phosphate minerals.
Chemical Methods: Processes like flotation and leaching may be employed to further separate and purify the phosphate minerals.
3. Drying:
After beneficiation, the phosphate concentrate is often dried to reduce moisture content. This step is crucial for downstream processing and storage.
4. Chemical Processing:
The dried phosphate concentrate is then typically treated with acids to produce phosphoric acid. Phosphoric acid is a key intermediate in the production of various phosphate compounds.
5. Granulation:
In fertilizer production, phosphate powder may be converted into granules for easier handling, storage, and application. Granulation is often done by adding binders and shaping the powder into granules.
6. Formulation:
Depending on the intended application, the phosphate powder or granules may be further processed and formulated. For example, in the production of detergents, phosphates may be combined with other ingredients to create the final product.
7. Quality Control:
Throughout the processing stages, quality control measures are implemented to ensure the desired specifications and purity levels are met.
8. Packaging:
The processed phosphate product is packaged for distribution. Packaging may vary depending on the end use, such as bags for fertilizers or bulk containers for industrial applications.
The specific steps and methods can vary based on the type of phosphate minerals present, the desired end product, and the technological processes employed by a particular facility. Additionally, environmental considerations, including the management of by-products and waste, are crucial in the phosphate processing industry to minimize environmental impact.
WHO WE ARE?
SBM Ultrafine Powder Technology Co., Ltd. is one of the premier manufacturers for equipment in the mining, grinding, coating,packing, recycling and process industries.
With SBM Ultrafine Powder Technology unique knowledge and innovative solutions, SBM helps many customers improve their operational efficiency, reduce risks and increase profitability.
SBM Ultrafine Powder Technology products can be divided into
crushing equipment, grinding equipment, drying equipment, screening equipment, conveying equipment and
auxiliary equipment.
SBM Ultrafine Powder Technology products have passed the quality system certification of ISO9001:2008, and the European CE certificate.
SBM sincerely welcome local distributors join us together to shape SBM Ultrafine Powder Technology brand and delivery high value-added equipment products in the global market around world.
SBM Ultrafine Powder Technology is an international high-tech enterprise which integrates the research and development, production and sales.
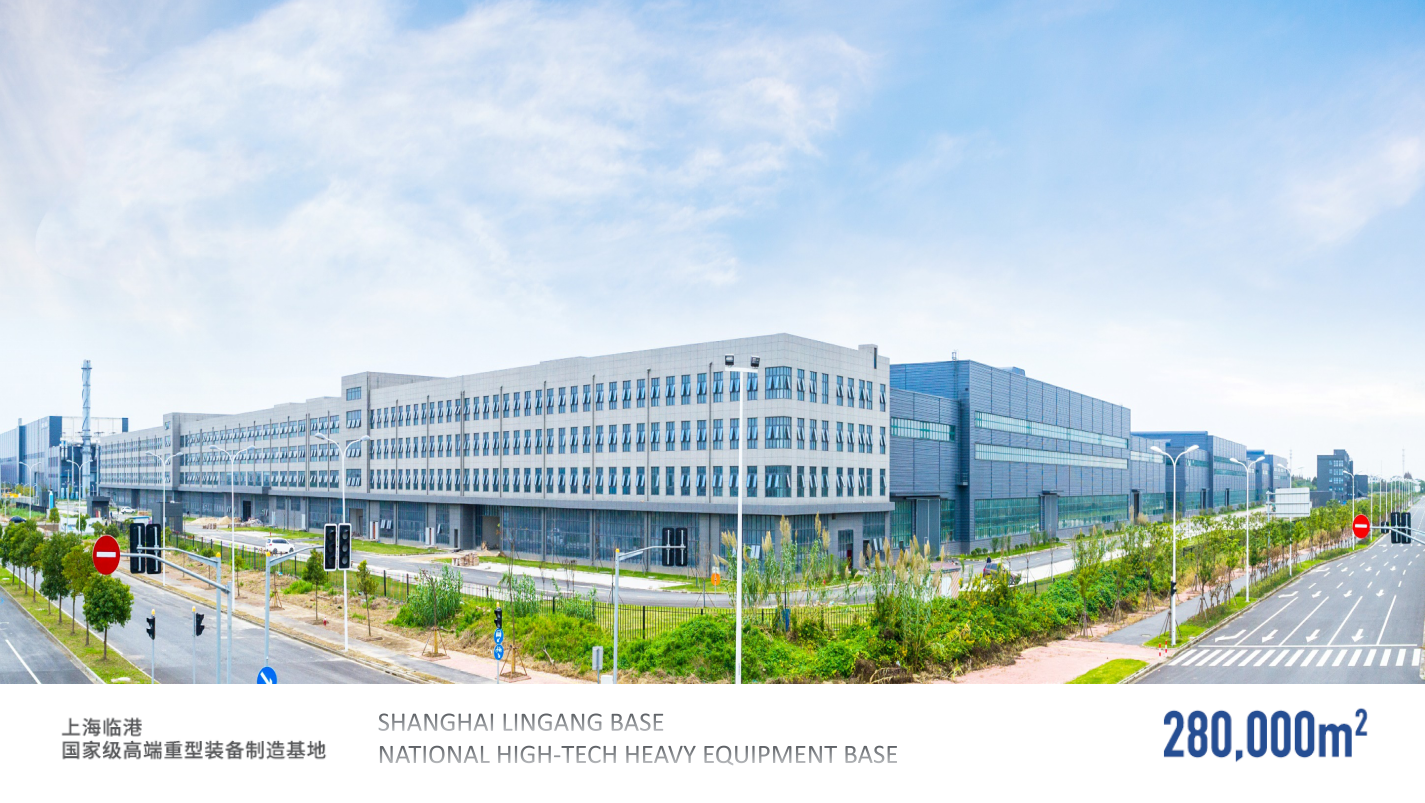
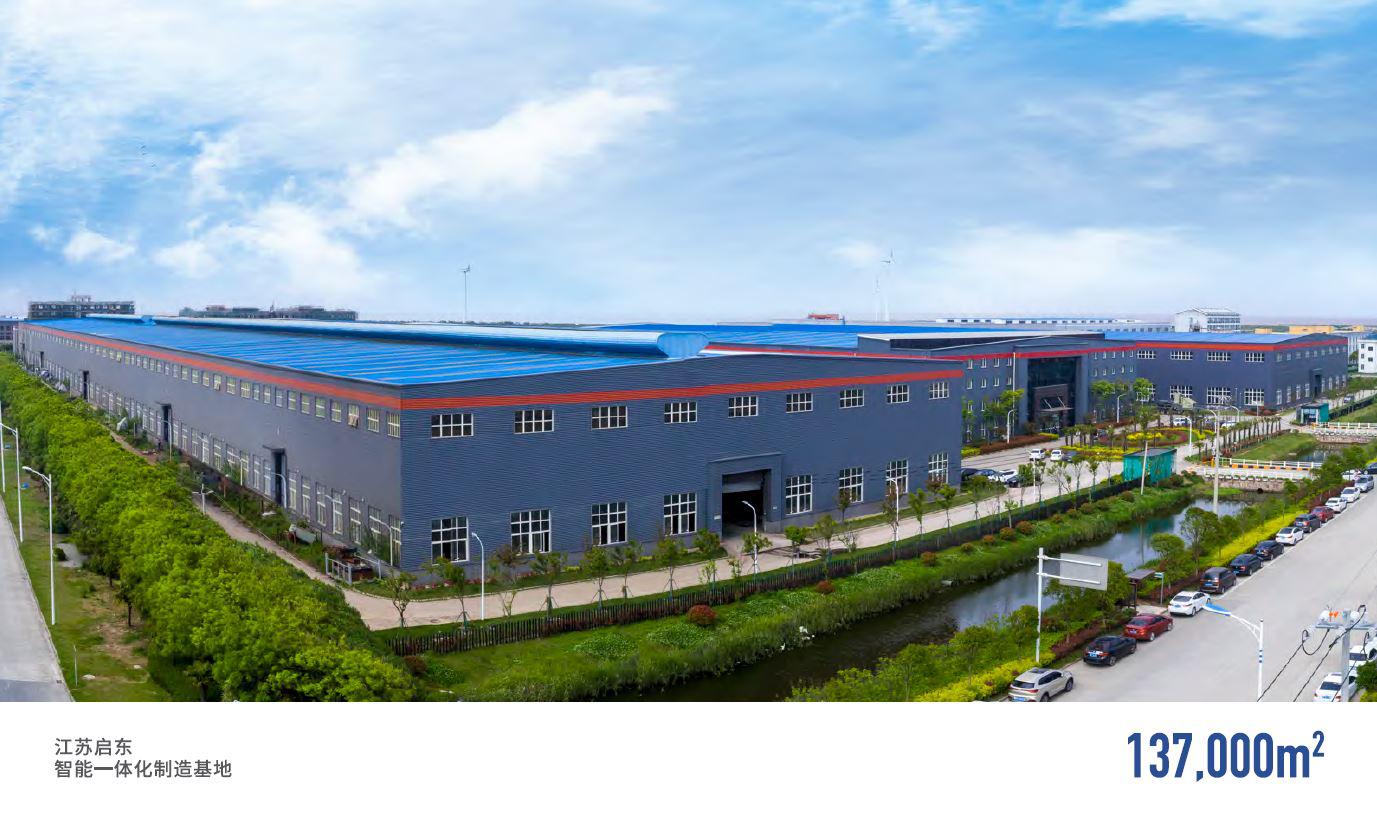
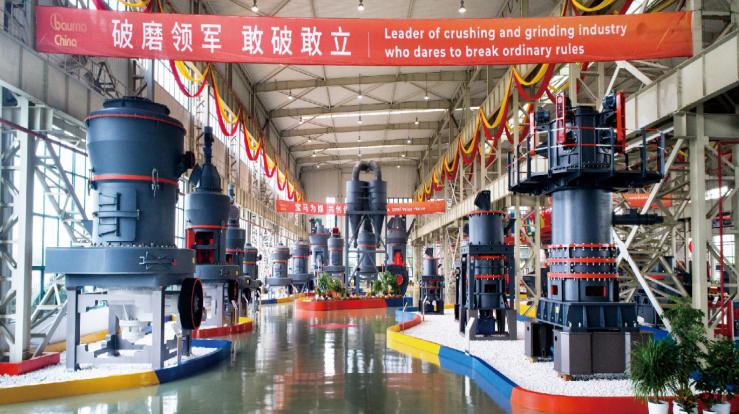



HOW TO BUY?
- 1. Engineering project design
- 2. Equipment purchasing and manufacturing
- 3. Engineering project construction
- 4. Installation and Commissioning service
- 5. After-sales service
WHICH MODELS CAN BE SELECTED FOR PROCESSING ULTRA-FINE POWDER?
HGM grinding mill: 74-5 micron(200-2500 mesh); D97=5 micron
YGM Raymond mill: 613-33 micron(30-325 mesh); D90=30 micron
CLUM vertical roller mill: 20-5 micron(600-3000 mesh); D50=2 micron D97=4 micron
HOW TO GET THE LATEST QUOTATION?
You can leave a message online or contact
SBM Ultrafine Powder Technology directly:
WhatsApp: +8613512155195






